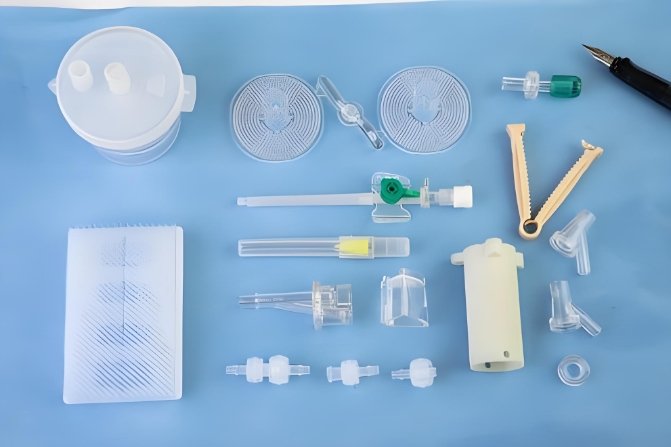
Medical devices require precision and safety. Medical injection molding ensures high-quality, sterile, and durable parts. A skilled mold maker plays a vital role in producing reliable components.
1. What is Medical Injection Molding?
The Basics
Medical injection molding creates plastic parts for healthcare. It ensures accuracy, consistency, and sterility. A mold maker designs precise molds for production.
Why It’s Important
- Produces sterile medical components
- Ensures accurate dimensions
- Reduces manufacturing errors
2. Key Benefits of Medical Injection Molding
High Precision
Every medical tool requires exact specifications. Medical injection molding provides tight tolerances. A mold maker ensures accuracy.
Sterility and Biocompatibility
Medical plastics must be safe for the body. Medical injection molding uses biocompatible materials. A mold maker selects FDA-approved plastics.
Cost-Effective Production
Large-scale production lowers costs. Medical injection molding offers efficient, high-volume manufacturing. A mold maker optimizes the process.
Lightweight and Durable
Plastic medical parts are lighter than metal. Medical injection molding creates strong, impact-resistant products. A mold maker ensures longevity.
Custom Designs
Complex shapes improve functionality. Medical injection molding allows custom designs. A mold maker tailors molds to unique specifications.
3. Applications of Medical Injection Molding
Surgical Instruments
Sterile tools must be reliable. Medical injection molding produces precision surgical instruments. A mold maker ensures durability.
Examples:
- Scalpel handles
- Forceps
- Clamps
Implantable Devices
Biocompatibility is crucial. Medical injection molding creates safe implants. A mold maker selects medical-grade plastics.
Examples:
- Pacemaker housings
- Artificial joints
- Dental implants
Drug Delivery Systems
Accurate dosing saves lives. Medical injection molding ensures precision in drug delivery. A mold maker designs high-accuracy molds.
Examples:
- Insulin pens
- Inhalers
- Syringe plungers
Diagnostic Equipment
Medical testing requires accuracy. Medical injection molding produces diagnostic components. A mold maker ensures high-quality parts.
Examples:
- Test tubes
- Lab trays
- Sample collection containers
Prosthetics and Orthopedic Devices
Comfort and durability matter. Medical injection molding helps create lightweight, strong prosthetics. A mold maker ensures custom designs.
Examples:
- Prosthetic limbs
- Braces
- Joint supports
4. Materials Used in Medical Injection Molding
Common Medical-Grade Plastics
A mold maker selects the right materials for safety and performance.
- Polycarbonate (PC) – High strength and clarity
- Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) – Biocompatible and heat-resistant
- Polypropylene (PP) – Flexible and chemical-resistant
- Silicone – Soft and flexible for implants
Why Material Choice Matters
- Ensures patient safety
- Maintains product durability
- Meets medical regulations
5. Cleanroom Manufacturing for Sterile Products
What is a Cleanroom?
It is a controlled environment. Medical injection molding requires strict cleanliness. A mold maker follows precise manufacturing protocols.
Why Cleanrooms are Essential
- Prevents contamination
- Ensures regulatory compliance
- Maintains product quality
6. Micro-Molding for Tiny Medical Parts
What is Micro-Molding?
It produces extremely small parts. Medical injection molding ensures high accuracy. A mold maker creates precise micro molds.
Applications
- Miniature surgical tools
- Catheter tips
- Hearing aid components
7. Single-Use vs. Reusable Medical Components
Why Use Single-Use Medical Tools?
Hospitals need disposable, sterile tools. Medical injection molding produces them efficiently. A mold maker ensures quality.
Reusable Medical Parts
Some medical devices must be sterilized and reused. Medical injection molding allows durable designs. A mold maker selects heat-resistant plastics.
Examples:
- Surgical instrument handles
- Blood pressure cuffs
- Monitoring device casings
8. Multi-Shot Molding for Complex Parts
What is Multi-Shot Molding?
It combines different materials in one part. Medical injection molding uses this method for improved function. A mold maker ensures perfect bonding.
Applications
- Soft-touch syringe grips
- Dual-layer medical tubing
- Ergonomic handles
9. Compliance with Medical Regulations
Why Compliance is Important
Medical parts must meet strict standards. Medical injection molding follows industry regulations. A mold maker ensures compliance.
Key Regulations
- FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration)
- ISO 13485 (Medical Device Quality)
- USP Class VI (Biocompatibility)
10. Rapid Prototyping for Faster Development
Why Prototyping Matters
New medical devices require testing. Medical injection molding enables rapid prototyping. A mold maker refines designs before mass production.
Prototyping Techniques
- 3D printing
- Soft tooling
- Small-batch molding
11. Automation for High-Efficiency Manufacturing
How Automation Helps
Modern machines improve efficiency. Medical injection molding now relies on robotics. A mold maker programs automated systems.
Automation Benefits
- Reduces human error
- Increases production speed
- Enhances consistency
12. Sustainable Medical Injection Molding
Eco-Friendly Manufacturing
Hospitals generate plastic waste. Medical injection molding now includes sustainable solutions. A mold maker selects biodegradable materials.
Green Medical Plastics
- Recycled PET
- Biodegradable polymers
- Plant-based resins
13. Advanced Cooling Systems for Faster Production
Why Cooling Matters
Faster cooling increases efficiency. Medical injection molding uses advanced cooling methods. A mold maker ensures even temperature distribution.
Cooling Techniques
- Conformal cooling channels
- Water-assisted cooling
- Copper-based inserts
14. Gas-Assisted Molding for Lightweight Parts
What is Gas-Assisted Molding?
It creates hollow parts. Medical injection molding reduces weight and material use. A mold maker ensures even thickness.
Applications
- Prosthetic components
- Syringe plungers
- Lightweight casings
15. The Future of Medical Injection Molding
What’s Next?
Technology keeps improving. Medical injection molding will use AI and smart materials. A mold maker will integrate automated quality control.
Upcoming Trends
- AI-driven inspection
- Fully automated molding lines
- Smart medical materials
Medical injection molding is essential for healthcare. It ensures precision, sterility, and efficiency. Skilled mold makers create high-quality medical components, advancing patient care and medical innovation.
